Yellow fever is an acute viral hemorrhagic disease found in tropical and subtropical areas in South America and Africa. The WHO estimates that yellow fever causes 200,000 illnesses and 30,000 deaths every year in unvaccinated populations, with around 90% of the infections occurring in Africa.
In most cases, yellow fever presents with fever, nausea, and pain that generally subsides after several days. In some patients (approximately 15%), a toxic phase follows, in which liver damage with jaundice (which gives the disease its name) can occur and lead to death. Approximately 20%–50% of patients who experience the toxic phase die, making the overall fatality rate for yellow fever around 3–7%.* No therapy or treatment is available for yellow fever, but vaccinations do exist.
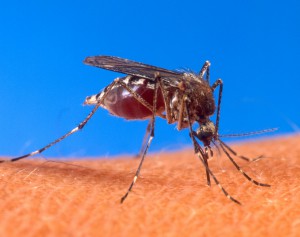
Vector insects
Aedes aegypti is the primary vector for yellow fever; however, other mosquitoes such as Aedes albopictus (Asian tiger mosquito) can also carry the virus.
Resources
Learn more about Yellow Fever disease
Quick Links
Contact a Valent BioSciences public health representative.
Contact Us